
site-local addresses (FEC0::/48) - deprecated.globally unique addresses and can be used to connect to addresses with global scope anywhere.
Packets addressed to a unicast address are delivered only to a single interface. Compared to IPv4 decimal representation of network mask cannot be used.Īs you can see there are no Broadcast addresses in ipv6 network, compared to IPv4 broadcast functionality was completely replaced with multicast. IPv6 prefix is written in address/prefix-length format. Otherwise, you could not determine the number of 0 bits represented by each instance of a double-colon

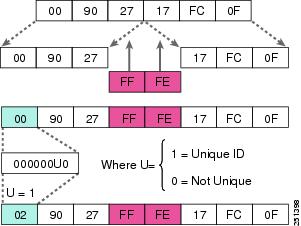
Note: Zero compression can only be used once. These contiguous sequence can be compressed to :: 2001:470:1f09:131 ::9 IPv6 address can be further simplified by removing leading zeros in each block:Īs you can see IPv6 addresses can have long sequences of zeros. The resulting representation is called colon-hexadecimal. IPv6 addresses are represented a little bit different than IPv4 addresses.įor IPv6, the 128-bit address is divided in eight 16-bit blocks, and each 16-bit block is converted to a 4-digit hexadecimal number and separated by colons. One difference between IPv6 and IPv4 addressing is that IPv6 automatically generates a link-local IPv6 address for each active interface that has IPv6 support. other (all other addresses, including the obsoleted site-local addresses, and RFC 4193 unique local addresses they all are treated as global unicast).There are multiple IPv6 address types, that can be recognized by their prefix.
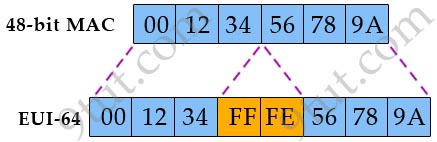
IPv6 address syntax and types are described in RFC 4291. IPv6 uses 16 bytes addresses compared to 4 byte addresses in IPv4.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
